As the demand for energy storage solutions continues to rise, a significant shift is anticipated in the battery industry. Experts are now predicting that "Lead Acid Replaces Lithium Batteries" by 2025, marking a pivotal change in how we approach energy solutions for various applications. Renowned industry expert Dr. Emily Johnson notes, "The resurgence of lead acid technology is driven by its cost-effectiveness and sustainability. It offers a reliable alternative to lithium batteries, especially in scenarios where recycling and lifespan are crucial factors."
This forecast is grounded in several key advantages associated with lead acid batteries, including their lower production costs and well-established recycling processes. As companies and consumers alike prioritize environmental sustainability, lead acid batteries are poised to reclaim their position in the market that has been largely dominated by lithium-ion technology in recent years. Furthermore, advancements in lead acid technology have significantly improved their performance metrics, making them an increasingly viable option for a variety of applications.
In conclusion, the anticipated transition from lithium to lead acid batteries represents not just a technological shift, but also a movement towards more sustainable and economically viable energy storage solutions. The industry is on the brink of a transformative era, and as Dr. Johnson emphasizes, "The future of energy storage may no longer be in lithium but in the familiar yet innovative realm of lead acid technology.
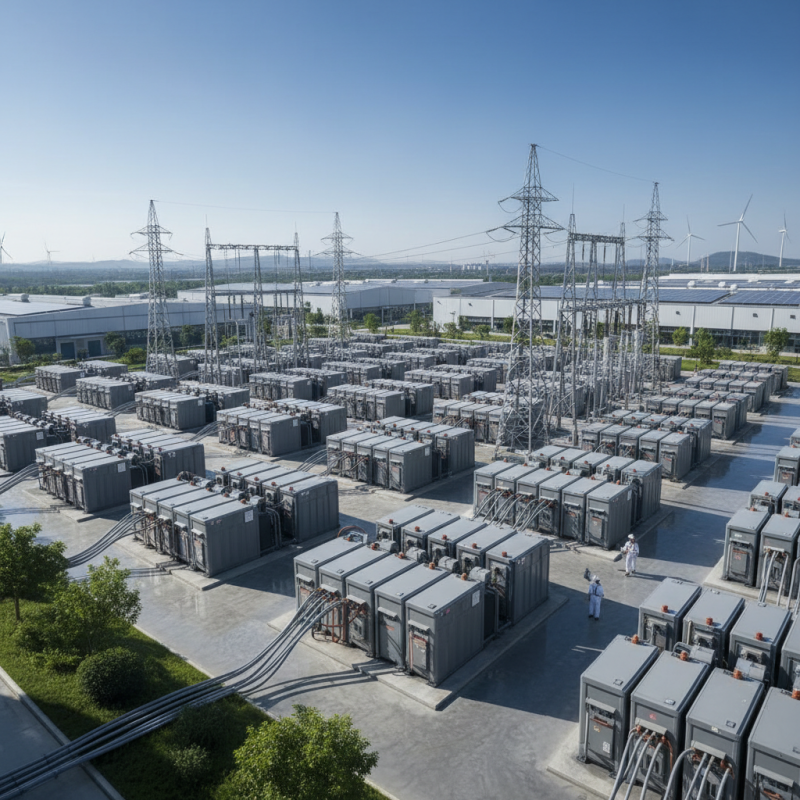


Recent advancements in lead acid battery technology are positioning these traditional power sources as serious contenders to lithium batteries by 2025. Innovations such as enhanced energy density and improved cycle life have significantly increased their appeal for various applications, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. New manufacturing techniques have also reduced the overall weight and size of lead acid batteries, making them more versatile for modern use.
**Tips:** When considering lead acid batteries for your projects, focus on choosing those with optimized designs to enhance performance and lifespan. Regular maintenance is essential; check electrolyte levels and ensure connections are clean to prevent efficiency losses.
The environmental impact of lead acid batteries is another critical factor driving this shift. With the increasing focus on sustainability, innovations in recycling processes have made it easier to reclaim materials from discarded batteries, thus reducing waste and resource consumption. This not only supports a circular economy but also alleviates some environmental concerns associated with battery disposal.
**Tips:** To contribute to sustainability, always recycle your old batteries through certified programs and keep informed about local regulations regarding battery disposal.
The transition from lithium to lead-acid batteries by 2025 raises important considerations regarding performance attributes. Lithium batteries are renowned for their higher energy density, which allows them to store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. This quality has made lithium suitable for applications requiring compact power sources, such as electric vehicles and portable electronics. Additionally, lithium batteries typically offer longer cycle lives and faster charging capabilities, enhancing their attractiveness for users seeking efficiency and reliability.
In contrast, lead-acid batteries, while historically favored for their cost-effectiveness and robust design, present significant limitations in energy density and weight. However, advancements in technology are bridging these gaps. Newer lead-acid models feature improved discharge rates and cycle performance, making them competitively viable in specific applications such as renewable energy storage and backup power systems. Their ability to handle high discharge rates while maintaining stability also makes them an appealing alternative in certain contexts, despite their heavier weight and shorter lifespan compared to lithium options. As the industry evolves, a careful comparative analysis will be essential to guide consumer choices based on performance needs and application requirements.
| Dimension | Lead Acid Batteries | Lithium Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 30-50 | 150-250 |
| Cycle Life (Cycles) | 500-800 | 2000-3000 |
| Charging Time (Hours) | 8-12 | 1-3 |
| Operating Temperature (°C) | -20 to 50 | -20 to 60 |
| Weight (kg for 12V, 100Ah) | 30 | 14 |
| Cost ($/kWh) | 150-200 | 300-600 |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, recyclable | Higher, complex recycling |
The projected growth of lead-acid battery usage by 2025 reflects a significant shift in the energy storage landscape. The demand for lead-acid batteries is expected to surge, driven by their affordability and reliability in various applications. Market analysis reveals that the automotive lead-acid battery sector alone is set to rise from approximately USD 12.54 billion in 2024 to USD 15.90 billion by 2033. This consistent growth suggests that lead-acid batteries will continue to play a critical role, particularly in vehicles and energy storage solutions.
Additionally, the lead-acid battery recycling market shows promising signs of expansion, with its size exceeding USD 12.1 billion in 2024 and projected to grow at a CAGR of 9% through 2034. Increasing awareness of sustainability and the need for eco-friendly energy solutions will likely contribute to this momentum. Coupled with advancements in technology, these trends indicate a robust future for lead-acid batteries, suggesting they will outpace lithium batteries in various applications by 2025.
This chart illustrates the projected growth of lead acid battery usage from 2018 to 2025, indicating a significant increase as they are expected to replace lithium batteries in various applications.
The shift from lithium batteries to lead acid batteries is poised to bring significant environmental benefits that could transform energy storage solutions. Lead acid batteries are more sustainable due to their higher recycling rates – nearly 99% can be recycled, compared to the lower rates associated with lithium-ion batteries. This ensures that lead is reused, minimizing environmental waste and reducing the need for new raw materials, which often involve harmful mining practices.
Moreover, lead acid batteries are less harmful to the environment during their production and disposal. The manufacturing process for lead acid batteries generates fewer greenhouse gases, and their simpler chemistry allows for safer and more environmentally friendly recycling processes. As the global community increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the transition to lead acid batteries could significantly reduce the ecological footprint of energy storage, paving the way for cleaner and more responsible energy solutions in the coming years.
The transition from lithium to lead acid batteries is being driven by key industries embracing digital technologies and smart energy infrastructure. As industries worldwide prioritize sustainability and efficiency, lead acid batteries offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for energy storage and transportation. The implementation of smart grids and energy management systems enhances the appeal of lead acid batteries by integrating them into a more responsive and efficient energy ecosystem.
In terms of market dynamics, Germany stands out with its accelerating transformation in the transportation sector. With ambitious goals for reducing carbon emissions, the push for lead acid batteries is becoming prominent as they provide a substantial reduction in upfront costs compared to lithium alternatives. Additionally, tropical battery technologies are emerging in regions such as Malaysia, where they promise to innovate energy storage and distribution systems, aligning with the growing demand for renewable energy solutions in the ASEAN region. This regional development further reflects the commitment to transitioning towards more sustainable energy sources globally.